Pagefile.sys - what is the file and how to delete it in Windows 11
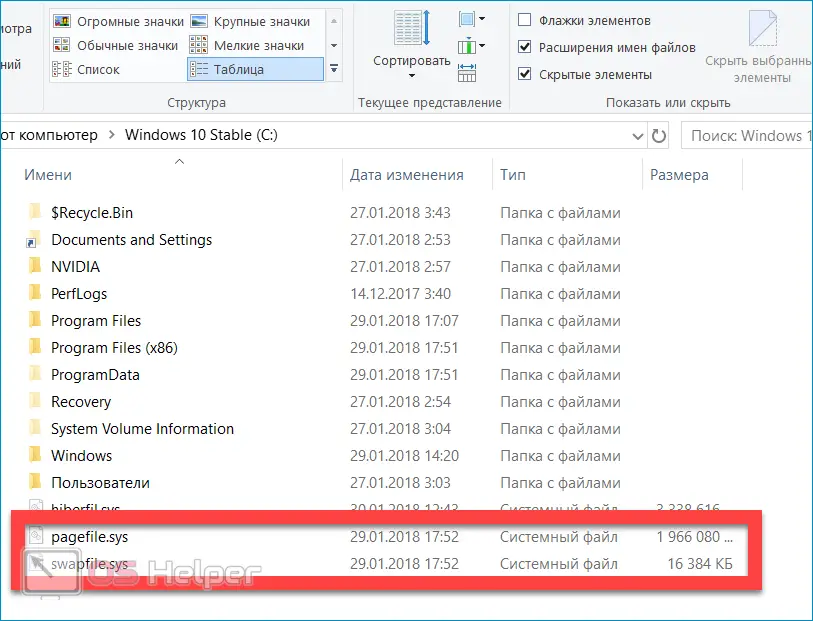
 Once having enabled the display of hidden objects in the operating system settings, the user can find a weighty Pagefile.sys file on the hard disk, which occupies several GB of space. Seeing it, many begin to wonder what the Pagefile.sys file is and how to delete it in Windows 11. If you also asked this question, then this article was created for you.
Once having enabled the display of hidden objects in the operating system settings, the user can find a weighty Pagefile.sys file on the hard disk, which occupies several GB of space. Seeing it, many begin to wonder what the Pagefile.sys file is and how to delete it in Windows 11. If you also asked this question, then this article was created for you.
What is the purpose of Pagefile.sys
Let's not languish - Pagefile.sys is a paging file that is used as a support for RAM. The space allocated on the HDD comes into effect when the programs running in the system begin to use the entire available amount of RAM - the OS automatically moves some of the information to the paging file, freeing up some RAM for other processes. As soon as the data moved to the FP is needed, the system will quickly remove it. This keeps the PC running smoothly.
Expert opinion
Daria Stupnikova
Specialist in WEB-programming and computer systems. PHP/HTML/CSS editor for os-helper.ru site .
Ask Daria We will talk further about whether it is worth disabling the paging file (and, accordingly, deleting the object in question).
Is it possible to get rid of Pagefile.sys?
In theory, Windows can run with FP completely disabled. In addition, abandoning it can be considered justified if the PC has 16-32 GB of RAM, but does not face time-consuming tasks. If the system has 2-4-8 GB of RAM, disabling the FP can cause the computer to periodically freeze and display notifications asking you to close this or that application.
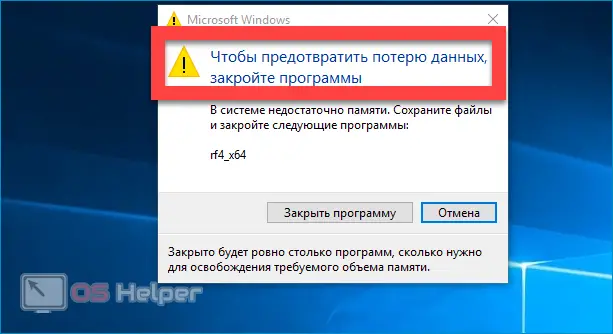
If you have firmly decided that you do not need the paging file that takes up disk space, you can delete it. Pagefile.sys will also disappear, freeing up valuable space. You don't need to worry about the consequences - for example, you can disable the FP, test the health of the OS and return swap if necessary.
See also: Unetbootin download in Russian for Windows 11
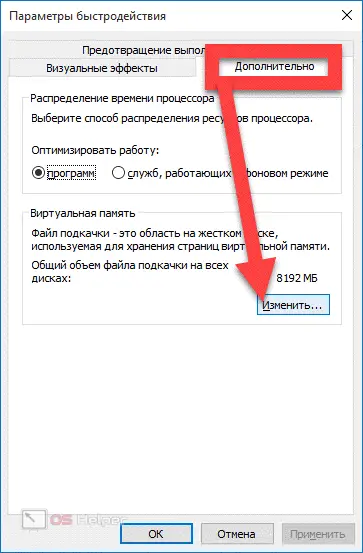
To delete a Pagefile, you need to perform the following sequence of actions:
- Press the key combination [knopka]Win[/knopka]+[knopka]Pause/Break[/knopka], open the "Advanced Options" on the left side of the window.
- Move to the "Advanced" section, find the "Performance" block, go to "Settings".
- Reopen "Advanced", get acquainted with the total amount of allocated space on all disks, click on "Change".
- Uncheck the box "Automatically select volume", activate the option "No paging file", click on "Set", apply the changes.
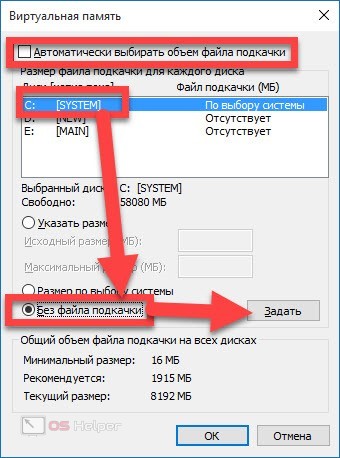
You only need to restart your PC for the changes to take effect. The object we are considering will be deleted automatically.
How to free up space?
If you do not want to give up swapping, but at the same time understand that it eats up all the free space, the problem can be solved without deleting the file itself - just reduce its size or even move it to another partition.
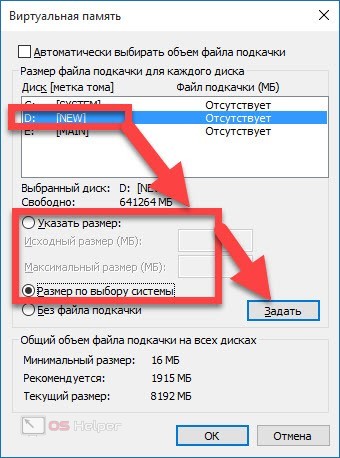
To resize a file or send it to another drive, you need to follow this instruction:
- We follow steps 1-4 of the previous guide - in this way we completely remove paging from the system hard drive.
- We select any other suitable disk in the list located at the top of the window, set the size of the future FP (you can entrust its determination to the system by selecting the option “Size at the choice of the system”), click on “Set”.
- To avoid moving the file, you can simply change its size - for this, instead of selecting the "Without FP" item, you need to activate "Specify Size" and insert those values \u200b\u200bthat seem acceptable to you.

It is recommended to place the FP on the disk that has the highest read and write speed - this will allow you to achieve maximum efficiency from the use of swap.
Video instruction
Below is a video that goes into more detail about Pagefile.sys - check it out if you don't want to read the article.
Conclusion
As you can see, there is no need to manually delete the Pagefile - operations with this system object are performed through the system performance settings. Due to the fact that the paging file is not something critical, you can test its volumes - change the initial and maximum sizes several times, and then check whether they will be enough for the normal operation of the OS.